Once you’ve deployed one or two Robotic Process Automation projects and proven RPA’s value, it’s time to strategically scale, continuously improve, and begin tackling the many possibilities for automation in your business. To most effectively do so, you will need to establish a Center of Excellence (CoE).
Forming an automation CoE is a critical step in achieving success with RPA, not just for large enterprises but also for small and mid-sized organizations. Why? A CoE acts as the central repository for best practices and guides the company in the maturation of your RPA program. This blog post provides practical guidance to help you establish your own automation CoE, plus offers 8 key metrics to consider as you measure the ongoing success of your RPA initiatives.
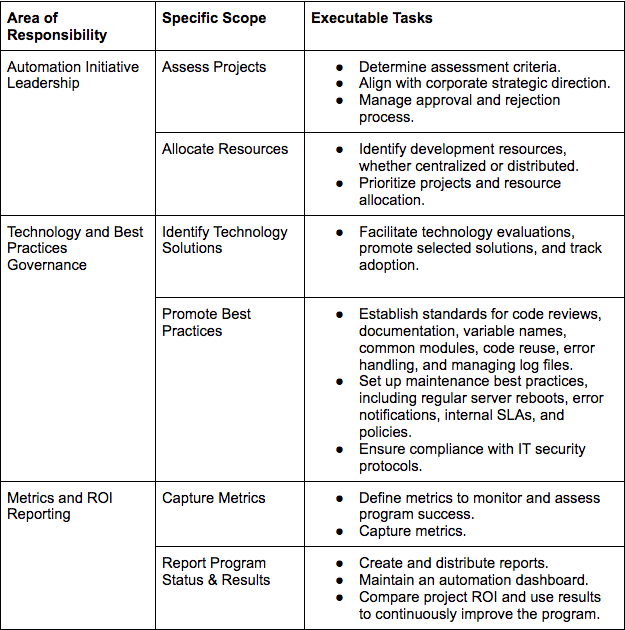
What are the Responsibilities of an Automation Center of Excellence (CoE)?
The CoE is responsible for coordinating projects and resources, serving as a repository for best practices and technical knowledge, and ensuring that the organization uses a common set of metrics for automation projects.
The chart below illustrates the core responsibilities and specific actions that should be expected of an automation CoE. Whether your organization builds its own CoE or works with an experienced partner like R-Path Automation, you will want to ensure that the CoE is able to deliver on each element contained herein.
Measuring the Success of Your RPA Program
As with any business investment, it’s important to clearly define which metrics you are trying to impact with your RPA initiative. Just remember to consider both hard and soft measures and be sure to align with the official metrics function(s) in your organization to ensure that your measures follow accepted definitions and data. Expanding the scope of automation will be easier and more compelling when your terms are clear and aligned with company norms.
Furthermore, make sure that you include metrics in day-to-day automation decisions. When metrics are owned by your Center of Excellence and have executive support, your organization is more likely to make consistent, data-driven decisions. You will also be better able to measure the impact of automation on corporate, department, and individual performance.
8 Common Benefits of RPA to Help Measure Your Success
The following are 8 common types of benefits organizations experience when deploying RPA. The metrics you define are unique to your business, so the brief descriptions that follow are intended to stimulate ideas for what measures might make sense for you.
1. Productivity Improvements
RPA undoubtedly improves productivity. Since productivity metrics are highly specific to each business though, it’s helpful to abstract a process from the day-to-day in order to understand what productivity means to you. Let’s say your business has a process for creating and delivering a report to your clients. If automating a step in the process reduces total time to delivery, or if it improves quality and reduces rework, this would be a productivity improvement. If, however, the automation simply reduces the time of one step of the process but fails to improve the overall throughput, it probably provides more of a cost or time savings than a real productivity improvement.
2. Cost Savings
RPA drives efficiencies that reduce or eliminate many operating and capital costs. RPA can also reduce the need to hire additional employees and upgrade or replace existing systems.
3. Time Savings
To measure time saved, compare the time spent per activity before and after automation. Note that while time saved is attractive because it can be measured, many organizations don’t necessarily save the costs associated with an employee’s salary because a job is not a task. Also keep in mind that time savings may have some other effect, like increased output or better customer service.
4. Accuracy Improvements
By eliminating human error from activities, you’ll inevitably see improved quality and/or reduced errors. Streamlined compliance processes are a great example of improved accuracy. In some situations, ensuring compliance avoids fines and, in some industries like healthcare, can accelerate the revenue cycle.
5. IT Security Improvements
Unfortunately, people are the greatest vulnerability risk in a security framework. Automation removes much of this risk and provides controls that can be easily inspected.
6. Employee Satisfaction
Many of the immediate opportunities for RPA are found in replacing the tedious, menial tasks that people do not want to perform anyway. Consider how to account for the effects of automation on employee satisfaction scores.
7. Customer Satisfaction
Look for reduced wait times and other process improvements that directly affect the customer experience. If your organization tracks customer satisfaction regularly through mechanisms like an NPS survey, try to identify improvements that might be attributed to faster service and/or fewer mistakes.
8. Revenue Growth
Consider how automating certain tasks reduces operating time and costs. Now imagine how that newfound bandwidth can be applied to developing new products or services, or simply enhancements to existing ones, that create new opportunities for revenue.
Ready to Embark on the Path to Automation?
At R-Path Automation, we make digital transformation accessible to mid-sized companies. Contact us today to get started and learn how to make your RPA program a success!

